|
Size: 11731
Comment:
|
Size: 10605
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 3: | Line 3: |
== Jenkins == Login info Jobs Settings, Plugins Binary builds require conda-build, constructor == Feedstocks == eman-dev eman-deps pydusa General instructions Existing feedstocks Files to edit: recipe/, conda-build.yaml, conda-forge.yaml conda create -n smithy conda-smithy -c conda-forge conda-smithy rerender More info in conda-smithy/README.md, conda smithy -h, conda-forge.org/docs New feedstocks conda-smithy/README.md, conda smithy -h == Docker ? == |
|
| Line 5: | Line 36: |
| ||||||'''Daily Builds'''|| ||{{http://10.10.11.176:8080/job/cron-matrix/label=linux/badge/icon?style=plastic&subject=Linux}}||{{http://10.10.11.176:8080/job/cron-matrix/label=mac/badge/icon?style=plastic&subject=Mac}}||{{http://10.10.11.176:8080/job/cron-matrix/label=win/badge/icon?style=plastic&subject=Win}}|| |
|
| Line 11: | Line 38: |
| 1. Dependency binaries are pulled from Anaconda. CMake uses conda environment location to find packages. 1. Make targets can be listed with {{{make help}}}. Some convenience targets are: {{{ $ make help The following are some of the valid targets for this Makefile: ... ..... ... ..... ... PythonFiles ... test-rt ... test-py-compile ... test-verbose-broken ... test-progs ... test-verbose ... ..... ... ..... }}} |
|
| Line 37: | Line 47: |
| 1. OpenGL detection when Anaconda's compilers are used is done using a cmake toolchain file. | 1. OpenGL detection when Anaconda's compilers are used is done using a [[https://github.com/cryoem/eman2/blob/master/recipe/cross-linux.cmake|cmake toolchain file]]. |
| Line 51: | Line 61: |
| Dependencies not available on anaconda or conda-forge are available on our channel [[https://anaconda.org/cryoem/|cryoem]]. The binaries are built and uploaded using [[https://conda-forge.org/|conda-forge's]] [[https://github.com/conda-forge/conda-smithy|conda-smithy]]. [[https://github.com/conda-forge/conda-smithy|conda-smithy]] takes care of generating feedstocks, registering them on !GitHub and online CI services and building conda recipes. Some of the packages available on [[https://anaconda.org/cryoem/|cryoem]]. 1. Not available on anaconda: ftgl and pydusa. 1. Forked and customized: openmpi (compiled with --disable-dlopen) and fftw-mpi (fftw compiled with mpi support). 1. Meta-package for EMAN dependencies: eman-deps. eman-deps depends on eman-deps-cli and gui packages, pyqt and pyopengl. 1. Meta-package for build machine setup: eman-packaging. Depends on conda, conda-build and forked constructor. It is used when setting up build machine environments. Forked constructor contains some customizations for eman. These are applied as patches in constructor-feedstock. |
Dependencies not available on anaconda or conda-forge are available [[https://anaconda.org/cryoem/|cryoem]]. The binaries are built and uploaded using [[https://conda-forge.org/|conda-forge's]] [[https://github.com/conda-forge/conda-smithy|conda-smithy]]. [[https://github.com/conda-forge/conda-smithy|conda-smithy]] takes care of generating feedstocks, registering them on !GitHub and online CI services and building conda recipes. Feedstocks * https://github.com/cryoem/eman-deps-feedstock * https://github.com/cryoem/pydusa-feedstock * https://github.com/cryoem/eman-feedstock ==== Initial Setup ==== ==== Maintenance ==== |
| Line 60: | Line 73: |
| Conda smithy uses tokens to authenticate with !GitHub and online CI services. | Conda smithy uses tokens to authenticate with !GitHub. |
| Line 94: | Line 107: |
| conda create -n smithy conda-smithy conda activate smithy |
|
| Line 100: | Line 115: |
| {{{#!wiki note TODO ABI compat, gcc dual ABI interface }}} |
|
| Line 108: | Line 119: |
| 1. !GitHub webhooks enable sending notifications when certain events like commit pushes happen. Generally, online services register webhooks automatically, but they need to be setup manually for Jenkins. 1. Every time a commit is pushed, source installation and binary builds are tested. |
1. !GitHub webhooks are setup to send notifications to blake. Blake forwards those to three build machines, although only Linux is sufficient. Linux runs the server that drives the the Jenkins jobs. |
| Line 112: | Line 122: |
| 1. Triggered by cron builds daily. | 1. --(Triggered by cron builds daily.)-- |
| Line 116: | Line 126: |
| 1. [[https://circleci.com/gh/cryoem/eman2|CircleCI]]: [[https://github.com/cryoem/eman2/blob/master/.circleci/config.yml|.circleci/config.yml]] 1. [[https://travis-ci.org/cryoem/eman2|TravisCI]]: [[https://github.com/cryoem/eman2/blob/master/.travis.yml|.travis.yml]] 1. [[https://ci.appveyor.com/|Appveyor]]: [[https://github.com/cryoem/eman2/blob/master/appveyor.yml|appveyor.yml]] |
1. --([[https://circleci.com/gh/cryoem/eman2|CircleCI]]: [[https://github.com/cryoem/eman2/blob/master/.circleci/config.yml|.circleci/config.yml]])-- 1. --([[https://travis-ci.org/cryoem/eman2|TravisCI]]: [[https://github.com/cryoem/eman2/blob/master/.travis.yml|.travis.yml]])-- 1. --([[https://ci.appveyor.com/|Appveyor]]: [[https://github.com/cryoem/eman2/blob/master/appveyor.yml|appveyor.yml]])-- |
| Line 120: | Line 130: |
| 1. Secrets like ssh keys are stored locally in Jenkins | |
| Line 123: | Line 134: |
| 1. Now, it is set on win, too. | |
| Line 131: | Line 143: |
| = Docker Images = 1. [[https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/cryoem/centos6|CentOS6:]] Was used to build CentOS 6 binaries on CentOS 7 to provide EMAN binaries compatible on older Linux machines. Not needed anymore because we build with anaconda's compilers and bundle the runtime libraries. 1. [[https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/cryoem/jenkins|Jenkins:]] Customized Jenkins server to setup on our build machines. 1. [[https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/cryoem/eman-deps|CircleCI:]] Docker images to use on CircleCI as a replacement for CircleCI's cache. |
= Jenkins Setup = Jenkins run command(?) Server on Linux, agents on Linux, Mac and Windows Jobs: * multi: Triggers job cryoem-eman2 on agents * cryoem-eman2: Test(?) and binary builds * eman-dev(?): Triggers new build of eman-dev === Jenkins Setup on Linux === Credentials PATH |
| Line 143: | Line 165: |
| 1. Triggers 1. GitHub webhooks 1. Cron 1. Binary build trigger |
|
| Line 149: | Line 167: |
| 1. Jenkins Docker image, docker-coompose or docker stack deploy | |
| Line 152: | Line 169: |
| 1. plugins 1. config, jcasc, config.xml, users.xml, jobs/*.xml?, gpg encrypt 1. Agent nodes setup, agent nodes auto-start |
1. Agent nodes setup |
| Line 156: | Line 171: |
| 1. Master only 1. Master and agent per machine 1. Single master and OS agents |
|
| Line 162: | Line 174: |
| 1. systemctl | |
| Line 168: | Line 179: |
| cron: 0 0 * * * bash /home/eman2/workspace/cronjobs/cleanup_harddisk.sh $ cat Desktop/docker.txt docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 jenkins/jenkins:lts docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 --restart unless-stopped jenkins/jenkins:lts docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 --restart unless-stopped -v /home/eman2/jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home jenkins/jenkins:lts docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 --restart unless-stopped -v /var/jenkins_home:/home/eman2/jenkins_home jenkins/jenkins:lts # Working docker run -u root -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 --restart unless-stopped -v /home/eman2/jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home jenkins/jenkins:lts docker run -u root -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 --restart unless-stopped -v /home/eman2/jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home jenkins docker run -d -u root -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 --restart unless-stopped -v /home/eman2/jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock jenkins/jenkins:lts sudo docker run -it -v /var/jenkins_home:/home/eman2/jenkins_home jenkins startup: right-click ??? |
|
| Line 184: | Line 182: |
| 1. plist docker run -d --name jenkins-master -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 -v /Users/eman/workspace/jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home --restart unless-stopped jenkins/jenkins:lts Auto startup: plist https://imega.club/2015/06/01/autostart-slave-jenkins-mac/ /Users/eman/Library/LaunchAgents |
|
| Line 192: | Line 185: |
| client 0 free swap space $ cat Desktop/docker.txt docker run -p 8080:8080 -v /Users/eman/workspace/jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home jenkins docker run -it -p 8080:8080 -v /Users/eman/workspace/jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home --restart unless-stopped jenkins # Working docker run -it -p 8080:8080 -v /Users/eman/workspace/jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home --restart unless-stopped jenkins/jenkins:lts # Blue Ocean docker run \ . -u root \ --rm \ -d \ -p 8080:8080 \ -v jenkins-data:/var/jenkins_home \ -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \ jenkinsci/blueocean # Latest docker run -d --name jenkins-master -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 -v /Users/eman/workspace/jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home --restart unless-stopped jenkins/jenkins:lts FROM jenkins/jenkins:lts COPY plugins.txt /usr/share/jenkins/ref/plugins.txt RUN /usr/local/bin/install-plugins.sh < /usr/share/jenkins/ref/plugins.txt plugins.txt: ace-editor:latest bouncycastle-api:latest branch-api:latest chef-identity:latest Settings: tokens slaves |
|
| Line 212: | Line 188: |
| Move jenkins_home http://tech.nitoyon.com/en/blog/2014/02/25/jenkins-home-win/ Run as service: Open Task Manager(Ctrl+Shift+Esc), New task, Browse to agent.jnlp and run as admin does this work? This is when starting via Web Launcher doesn't work. currently, task scheduler works need to have miniconda pn path, set it during miniconda installation, but do not(?) register python. While installing miniconda register python and add to PATH. Then, conda init in cmd (git init cmd.exe) and git windows (git init bash). And, maybe restart??? BUG: miniconda3 conda-build=3.17.8 adds vc14 even if python2 is requested in build reqs |
|
| Line 230: | Line 197: |
| == EMAN2 Docker images == | |
| Line 261: | Line 227: |
= Under Construction = EMAN2 is built with `conda-build` using binaries from https://anaconda.org, packaged into an installer with [[https://github.com/cryoem/constructor.git|constructor]] as of '''v2.2'''. 1. [[https://github.com/conda/conda|conda]] is the package manager. 1. https://anaconda.org is the online repository of binaries. 1. [[https://github.com/conda/conda-build|conda-build]] is the tool to build from source. 1. [[https://github.com/cryoem/constructor.git|constructor]] is the tool to package eman2 and dependency binaries into a single installer file. EMAN2 is distributed as a single installer which includes all its dependencies. However, EMAN2 is not available as a conda-package on https://anaconda.org. In other words it is not possible to install EMAN2 by typing {{{conda install eman2}}}. == Conda == Packages that are available on https://anaconda.org can be installed into any conda environment by issuing the command {{{conda install <package>}}}. Conda installs the package along with its dependencies. In order for packages to benefit from this automation, they need to be packaged in a specific way. That can be done with {{{conda-build}}}. {{{conda-build}}} builds packages according to instructions provided in a {{{recipe}}}. A recipe consists of a file with package metadata, {{{meta.yaml}}}, and any other necessary resources like build scripts, ({{{build.sh}}}, {{{bld.bat}}}), patches and so on. == Recipes, Feedstocks and anaconda.org channel: cryoem == Most of EMAN2 dependencies can be found on anaconda's channels, {{{defaults}}} and {{{conda-forge}}}. A few that do not exist or need to be customized have been built and uploaded to channel [[https://anaconda.org/cryoem/dashboard|cryoem]]. The recipes are hosted in separate repositories on [[https://github.com/cryoem/|GitHub]]. Every recipe repository follows the feedstock approach of [[http://conda-forge.github.io/|conda-forge]]. See [[https://github.com/cryoem?utf8=%E2%9C%93&q=-feedstock&type=&language=|here]] for a complete list. == Binary Distribution == === Constructor === Packaging is done with {{{constructor}}}, a tool for making installers from conda packages. In order to slightly customize the installers the project was forked. The customized project is at https://github.com/cryoem/constructor. The input files for {{{constructor}}} are maintained at --(https://github.com/cryoem/docker-images )-- https://github.com/cryoem/build-scripts. The installer has additional tools like {{{conda}}}, {{{conda-build}}}, {{{pip}}} bundled. The installer is setup so that the packages are kept in the installed EMAN2 conda environment cache for convenience. ==== Docker ==== Docker images and helper scripts are at --(https://github.com/cryoem/docker-images )-- https://github.com/cryoem/build-scripts. Command to run docker with GUI support, CentOS7: {{{ xhost + local:root docker run -it -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY cryoem/eman-nvidia-cuda8-centos7 # When done with eman xhost - local:root }}} :FIXME: Runs as root on Linux. `chown` doesn't work, the resulting installer has root ownership. |
Contents
Jenkins
Login info Jobs Settings, Plugins Binary builds require conda-build, constructor
Feedstocks
eman-dev eman-deps pydusa
General instructions Existing feedstocks Files to edit: recipe/, conda-build.yaml, conda-forge.yaml conda create -n smithy conda-smithy -c conda-forge conda-smithy rerender More info in conda-smithy/README.md, conda smithy -h, conda-forge.org/docs New feedstocks conda-smithy/README.md, conda smithy -h
Docker ?
Build System Notes
CMake
libpython can be linked statically or dynamically when python is built. It is important for python extensions to be aware of the type of linking in order to avoid segfaults. This can be accomplished by querying Py_ENABLE_SHARED.
1 python -c "import sysconfig; print(sysconfig.get_config_var('Py_ENABLE_SHARED'))"In EMAN, it is done in cmake/FindPython.cmake
OpenGL detection when Anaconda's compilers are used is done using a cmake toolchain file.
- glext.h file needed for OpenGL related module compilation is already present on Linux and Mac. On Windows, it is manually copied once into C:\Program Files\Microsoft SDKs\Windows\v6.0A\Include\gl. On Appveyor it is downloaded as part of env setup every time a test is run.
- Compiler warnings are turned off by default and can be turned on by setting ENABLE_WARNINGS=ON
1 cmake <source-dir> -DENABLE_WARNINGS=ON Setting compiler and linker options by include_directories, add_definitions that have global affects are avoided and target-focused design employing modern cmake concepts like interface libraries are used as much as possible.
Anaconda
Dependencies not available on anaconda or conda-forge are available cryoem. The binaries are built and uploaded using conda-forge's conda-smithy. conda-smithy takes care of generating feedstocks, registering them on GitHub and online CI services and building conda recipes.
Feedstocks
Initial Setup
Maintenance
Conda-smithy Workflow
Conda smithy uses tokens to authenticate with GitHub.
Conda-smithy commands:
1 conda create -n smithy conda-smithy 2 conda activate smithy 3 conda smithy init <recipe_directory> 4 conda smithy register-github <feedstock_directory> --organization cryoem 5 conda smithy register-ci --organization cryoem --without-azure --without-drone 6 conda smithy rerender --no-check-uptodate
Continuous Integration
GitHub webhooks are setup to send notifications to blake. Blake forwards those to three build machines, although only Linux is sufficient. Linux runs the server that drives the the Jenkins jobs.
- Binary builds on local build machines.
Manually triggered by including "[ci build]" anywhere in the last commit message. Manually triggered builds on master branch are uploaded as continuous builds and builds triggered from any other branch are uploaded to testing area.
Triggered by cron builds daily.
- Any branch in the form of "release-" triggers continuous builds without having to include "[ci build]" in the commit message. Once the release branch is ready, release binaries are manually copied from cont. builds folder into the release folder on the server.
- CI configurations files:
JenkinsCI: Jenkinsfile
- Secrets like ssh keys are stored locally in Jenkins
- Some env vars need to be set by agents:
- HOME_DIR, DEPLOY_PATH, PATH+EXTRA (to add miniconda to PATH).
- PATH+EXTRA is not set on win. (?)
- Now, it is set on win, too.
Launch method: via SSH Advanced: Prefix Start Agent Command: "D: && "- On windows for sh calls in jenkins to work "Git for Windows" might need to be installed.
Jenkins Setup
Jenkins run command(?)
Server on Linux, agents on Linux, Mac and Windows
Jobs:
- multi: Triggers job cryoem-eman2 on agents
- cryoem-eman2: Test(?) and binary builds
- eman-dev(?): Triggers new build of eman-dev
Jenkins Setup on Linux
Credentials
PATH
Under Construction
Jenkins Setup
- Jenkins master needs PATH prepended with $CONDA_PREFIX/bin
- docker-compose.yml at home dir in build machines
- Agent nodes setup
- Server and agent per machine vs single server and os agents
Linux
docker run -d -u root -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 --restart unless-stopped -v /home/eman2/jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock jenkins/jenkins:lts &
docker run -d -u root --name jenkins-master -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 --restart unless-stopped -v /home/eman2/jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -e PLUGINS_FORCE_UPGRADE=true -e TRY_UPGRADE_IF_NO_MARKER=true --restart unless-stopped cryoem/jenkins:dev
Mac
slave clock sync https://blog.shameerc.com/2017/03/quick-tip-fixing-time-drift-issue-on-docker-for-mac docker run --rm --privileged alpine hwclock -s
Windows
OPENGL: https://github.com/conda/conda-recipes/blob/master/qt5/notes.md
Distribution
Binaries on cryoem.bcm.edu
EMAN2 on anaconda.org
Under Construction
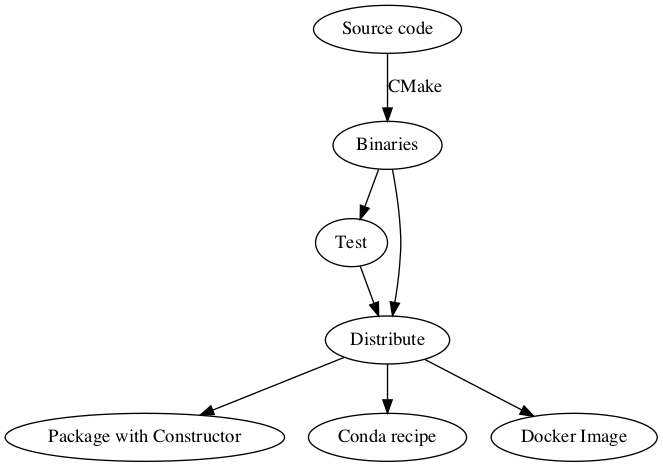
EMAN2 is built with conda-build using binaries from https://anaconda.org, packaged into an installer with constructor as of v2.2.
conda is the package manager.
https://anaconda.org is the online repository of binaries.
conda-build is the tool to build from source.
constructor is the tool to package eman2 and dependency binaries into a single installer file.
EMAN2 is distributed as a single installer which includes all its dependencies. However, EMAN2 is not available as a conda-package on https://anaconda.org. In other words it is not possible to install EMAN2 by typing conda install eman2.
Conda
Packages that are available on https://anaconda.org can be installed into any conda environment by issuing the command conda install <package>. Conda installs the package along with its dependencies. In order for packages to benefit from this automation, they need to be packaged in a specific way. That can be done with conda-build. conda-build builds packages according to instructions provided in a recipe. A recipe consists of a file with package metadata, meta.yaml, and any other necessary resources like build scripts, (build.sh, bld.bat), patches and so on.
Recipes, Feedstocks and anaconda.org channel: cryoem
Most of EMAN2 dependencies can be found on anaconda's channels, defaults and conda-forge. A few that do not exist or need to be customized have been built and uploaded to channel cryoem. The recipes are hosted in separate repositories on GitHub. Every recipe repository follows the feedstock approach of conda-forge. See here for a complete list.
Binary Distribution
Constructor
Packaging is done with constructor, a tool for making installers from conda packages. In order to slightly customize the installers the project was forked. The customized project is at https://github.com/cryoem/constructor. The input files for constructor are maintained at https://github.com/cryoem/docker-images https://github.com/cryoem/build-scripts.
The installer has additional tools like conda, conda-build, pip bundled. The installer is setup so that the packages are kept in the installed EMAN2 conda environment cache for convenience.
Docker
Docker images and helper scripts are at https://github.com/cryoem/docker-images https://github.com/cryoem/build-scripts.
Command to run docker with GUI support, CentOS7:
xhost + local:root docker run -it -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY cryoem/eman-nvidia-cuda8-centos7 # When done with eman xhost - local:root
:FIXME: Runs as root on Linux. chown doesn't work, the resulting installer has root ownership.